The Ankeniheny Zahamena Corridor (CAZ) represents a large part of the remnants of the dense evergreen rainforest, particularly at mid-altitude. The flora found here includes elements typical of this type of habitat, as well as species endemic to the East, including numerous orchid species and palm trees. The site is also rich in fauna. The corridor also boasts remarkable natural features such as waterfalls and hot springs, as well as landscapes of great tourist value. …
Archives: Aires protégées
Marojejy-Anjanaharibe Sud-Tsaratanana Corridor
COMATSA is essentially covered continuously by the medium-altitude evergreen rainforest. In its northern part, the flora includes several elements common in rainforests as well as numerous species restricted to the northern mountain ranges and local endemic species. This area has a great richness in fauna: 4 locally endemic amphibian species are recorded here with other species whose distribution is restricted. The site is also rich in chameleons and small mammals. The southern part is less rich in terms of flora, however, the represented flora includes endemic species of the Sambirano domain. The southern part is equally rich in fauna with considerable specific diversity in reptiles and amphibians; local endemic species are also recorded for both groups. …
Zombitse Voabasia
The Zombitse Vohibasia National Park belongs to the Western ecoregion, where flora and vegetation are significantly influenced by variations in soil types and geology. It exhibits remarkable diversity in both habitats and biodiversity. The park’s forest is divided into several forest blocks and harbors typical floristic species of the spiny thicket and dry dense forest. In terms of fauna, Zombitse Vohibasia has a locally endemic lemur species, the Hubbard’s sportive lemur. …
Nosy Ve Androka
The Nosy Ve-Androka Marine Park is included in the coral reef system of the Southwest region of Madagascar, recognized as one of the richest in tropical waters, and it houses the third-largest coral reef system in the world. It is composed of various marine habitats including reefs, moderately deep shoals dotted with coral shoals, and beaches. …
Nosy Hara
Nosy Hara National Park represents specific habitats such as coral reefs, mangroves, seagrass beds, and islets. These places are renowned as a nesting site for marine turtles of the Indian Ocean, feeding areas for threatened species such as the Dugong or the Fishing eagle, and as a refuge and breeding ground for the fish species in the park. Nosy Hara also houses the beautiful and intact coral reefs of the Mozambique Channel. Having both terrestrial and marine ecosystems, the park presents various important habitats as well as a variety of fauna and flora. …
Mangerivola
The flora of the site is still poorly known but seems to include typical elements of the forest in the region. On the other hand, the reserve has a great biological richness in fauna, especially for birds and amphibians. …
Kalambatritra
Half of the protected area is covered by forests, in two main adjacent massifs and several satellite fragments; the rest is composed of herbaceous vegetation. The flora found here includes typical and widespread elements of the evergreen humid dense forest and two locally endemic species are recorded. The protected area also has significant biological richness in terms of fauna; a lemur species currently classified as endangered is locally endemic there (Lepilemur wrightae). …
Galoko Kalobinono
The Galoko-Kalobinono PA belongs to the phytogeographic domain of Sambirano. In terms of flora, endemic species to the forests of the Northwest are found there, and the site is home to 14 local endemic species. Faunal species are characterized by the following groups in this area: herpetofauna, primates, and avifauna. …
Cap Sainte Marie
The Cap Sainte Marie Special Reserve represents the exceptional biodiversity of southwestern Madagascar. The floristic richness is mainly based on dwarf vegetation with typical elements characteristic of the spiny thicket; some locally endemic species such as Aloe millotti can even be found there. As for fauna, the site is home to the radiated tortoise (Astrochelys radiata) and the spider tortoise (Pyxis arachnoides), which are endemic and endangered species. …
Bombetoka
The Belemboka-Bombetoka protected area is dominated by the mangrove ecosystem, which develops on about twenty islets as well as on the west and east banks of the bay. Its flora includes typical elements of the dry dense forest, as well as species and habitats of freshwater and mangrove. In terms of fauna, the protected area has global importance for birds. …
Beza Mahafaly
The Bezà-Mahafaly Special Reserve and the surrounding forests represent the different existing formations in Southwest Madagascar, composed of species adapted to drought. In terms of flora, the site is home to several widespread woody species typical of riparian forest in the dry bioclimatic region. In terms of fauna, there is a high density of diurnal lemur species that have been the subject of long-term studies at the site, such as the ring-tailed lemur or lemur catta, and the Verreaux’s sifaka. …
Betampona
The Integrated Betampona Natural Reserve’s main habitat is the lowland evergreen rainforest. The flora found there includes endemic species and elements from the East, including 26 species of palms. The site is also known for its notable richness in fauna, despite its relatively small size. …
Andasibe Mantadia
Mantadia National Park is part of the Eastern ecoregion, which is among the most species-rich areas in the country. The park’s medium-altitude dense humid forest has a high biological diversity, including the largest lemur species in Madagascar, Indri indri, a rare frog species, and various orchids. …
Analamerana
The flora encountered in Analamerana includes typical elements of the dry dense forest and locally endemic species in the north. From a faunal point of view, due to its climate and the relatively bare character of a good part of its surface, the reserve does not promote the abundance of reptiles or amphibians. However, the site harbors an important population of Propithecus perrieri, which is a lemur species restricted to the extreme north of the island and is considered critically endangered on the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List. …
Analamazaotra
The park mainly houses a mid-altitude dense humid forest. Despite its small size, it has a high biological diversity for both fauna and flora. …
Ambohitantely
The Ambohitantely Special Reserve ensures the representation of the central terrestrial ecoregion. The Reserve is home to a palm species, the Dypsis oropedionis, which requires particular attention given its status within the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) and the pressures weighing on it. This palm is also among the conservation targets of the Protected Area (PA). …
Andranomena
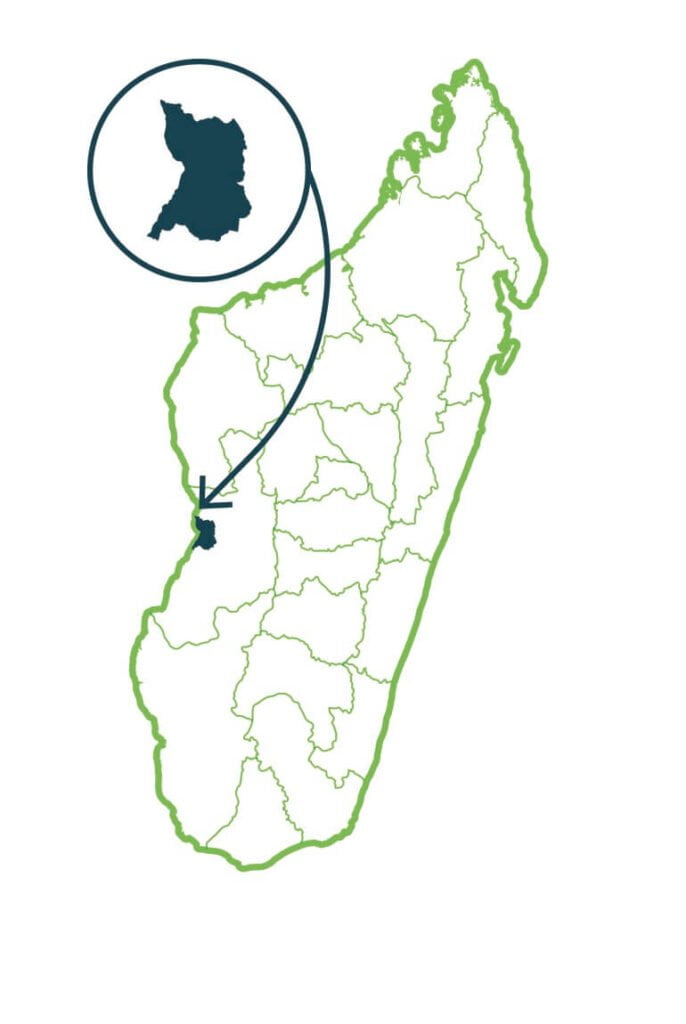
The northern part of the Special Reserve of Andranomena shelters a relatively dense dry forest while the central and southern parts present slightly degraded forms. In favor of some basins, there are also small lakes, mainly temporary, surrounded by grassy swamps. The southern and eastern limits are covered with secondary formations where some sacred baobabs remain. Among the flagship species, Andranomena is home to the flat-tailed turtle and the smallest primate in the world, the microcèbe of Mme Berthe. …
Lokobe
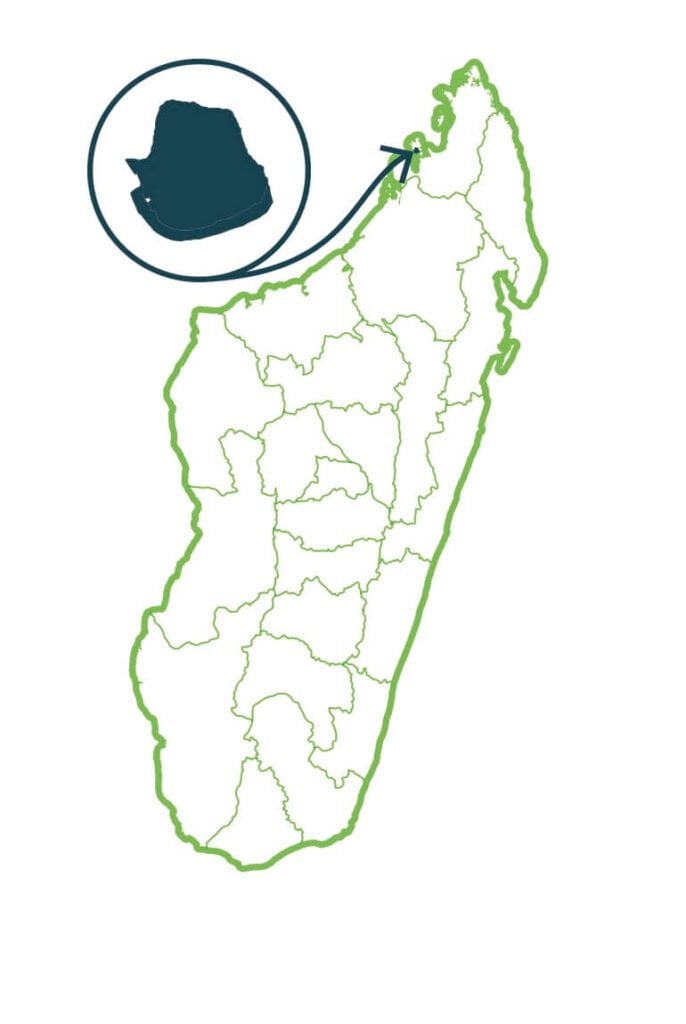
The Lokobe forest represents one of the last remnants of lowland dense evergreen forest in the Sambirano phytogeographic domain. Two main ecosystems are found in the park: the terrestrial ecosystem and the marine ecosystem. The terrestrial parcel of Lokobe shelters remarkable species like lemurs with very restricted distribution, and threatened species of palms such as Dypsis ampasindavae. The marine parcel located south of the terrestrial parcel is made up of coral reef and phanerogam meadows as well as a very small area of mangrove. …
Manongarivo
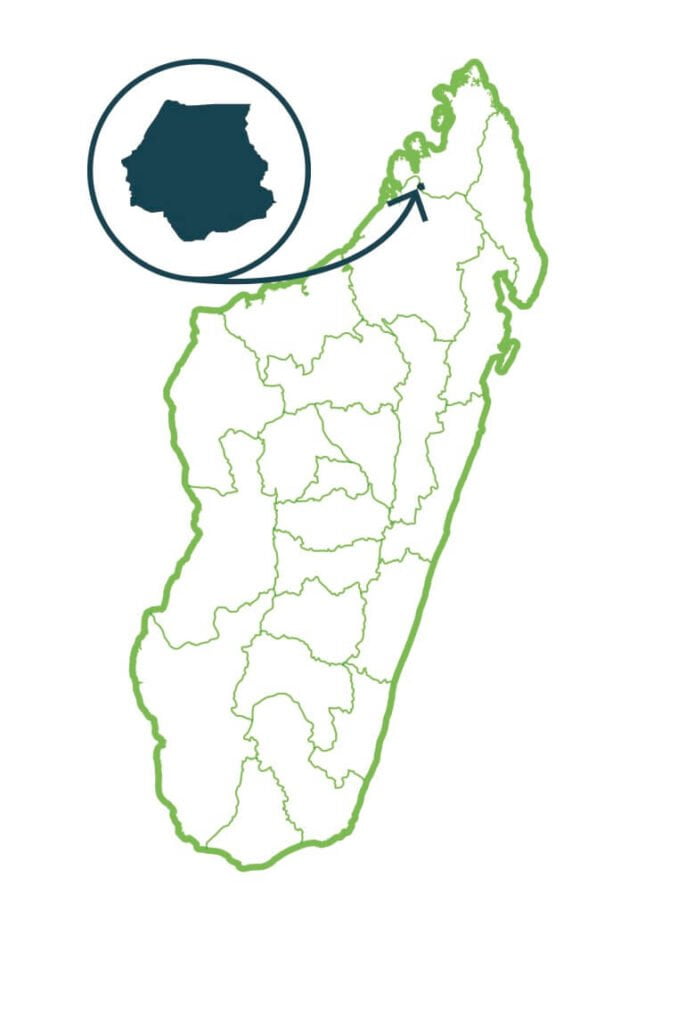
National Park of Lokobe and the Special Reserve of Manongarivo are the last representatives of the dense forest of the phytogeographic domain of Sambirano. With the different vegetal formations that are found there, the reserve registers an exceptionally rich biological diversity as much from the floristic point of view as faunistic. From a floristic point of view, it’s to should be noted that the vegetation of the reserve is essentially forest with several species restricted to the dense humid forests of the North. For the fauna, it shelters lemurs reminding its belonging to the domain of Sambirano, notably the Avahi and the microcèbe of Sambirano. It is also home to two species of chameleons of the genus Brookesia locally endemic. …
Nosy Mangabe
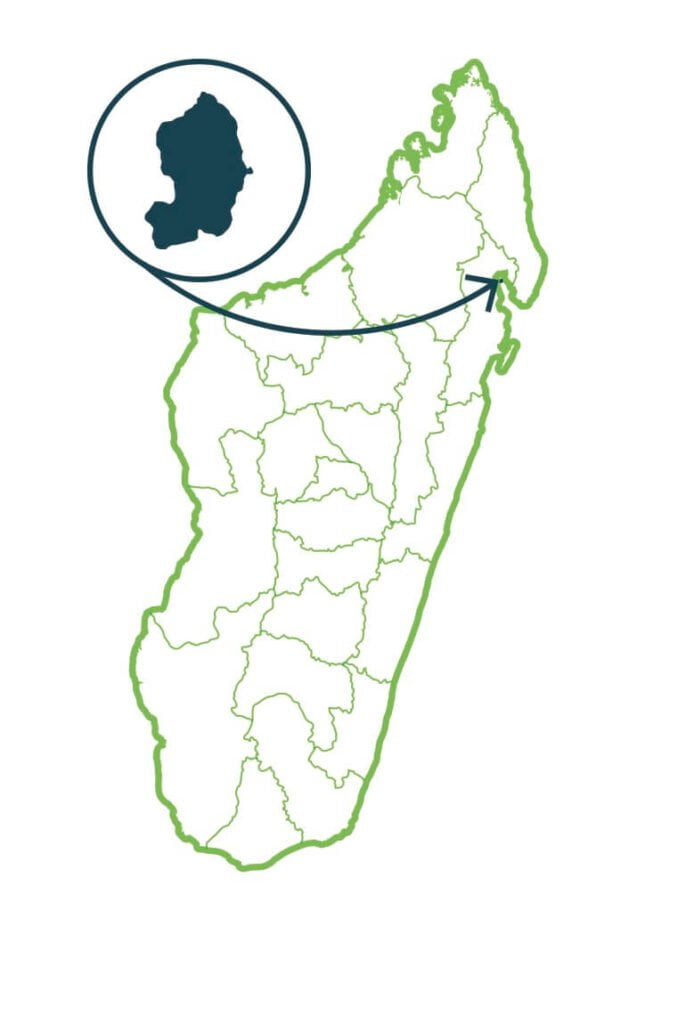
The park is formed by four islets: Nosy Mangabe, Nosy Milomboko, Nosy Haramy and Nosy Ravina. The islet Nosy Mangabe is totally covered with natural forests from the sea level to its highest peak. In terms of biodiversity, we can say that Nosy Mangabe, despite its relatively small size, is quite rich. The insularity implies a relatively reduced animal diversity in comparison with other forests of the same type on the mainland. However, reptiles are particularly abundant, probably due to the low level of disturbance and the scarcity and absence of certain species of raptor birds and carnivorous mammals. The park also supports local endemic species of amphibians: “Rhombophryne mangabensis” and “Stumpffia dolchi”. …




