Flagship Species
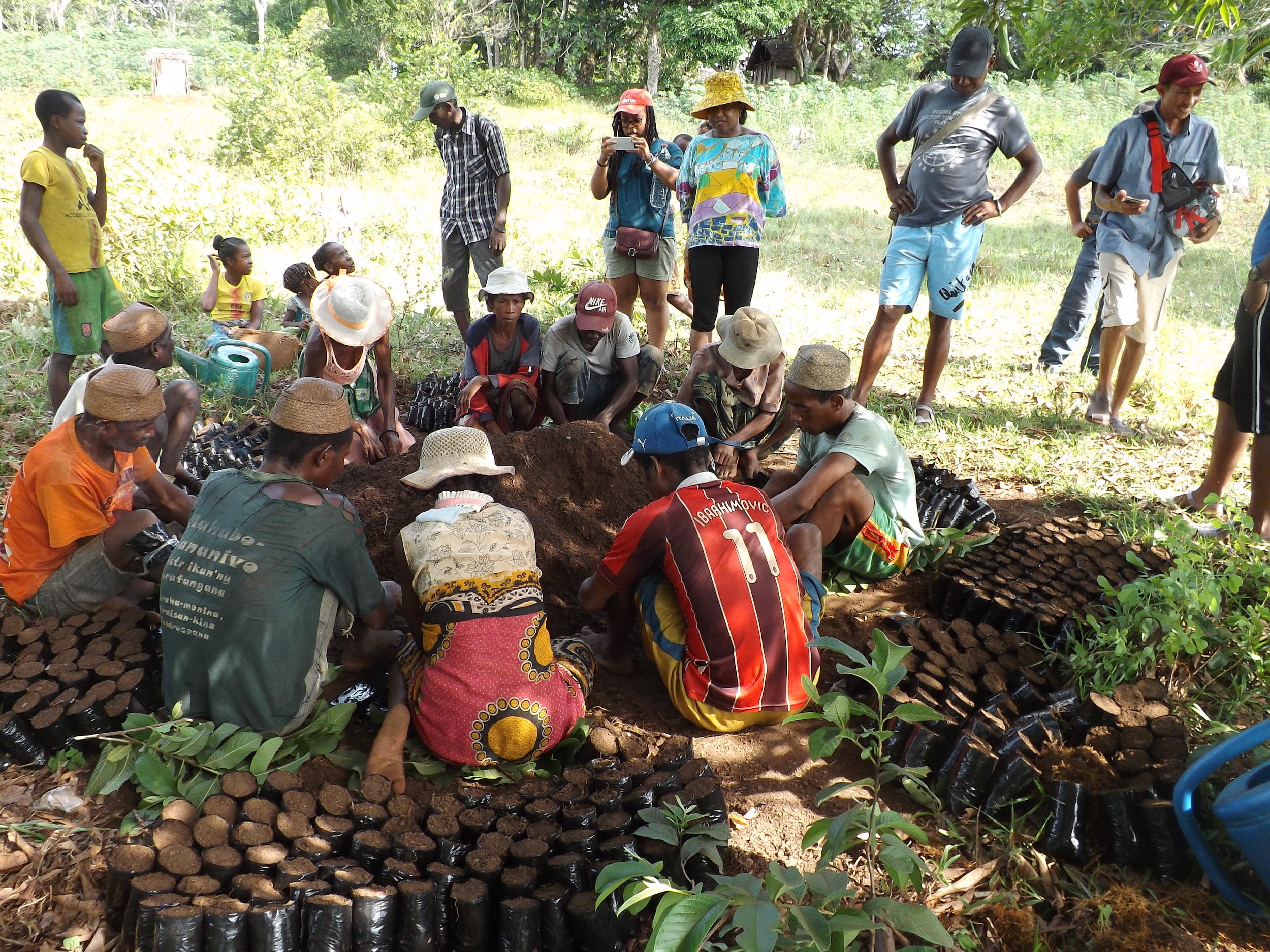
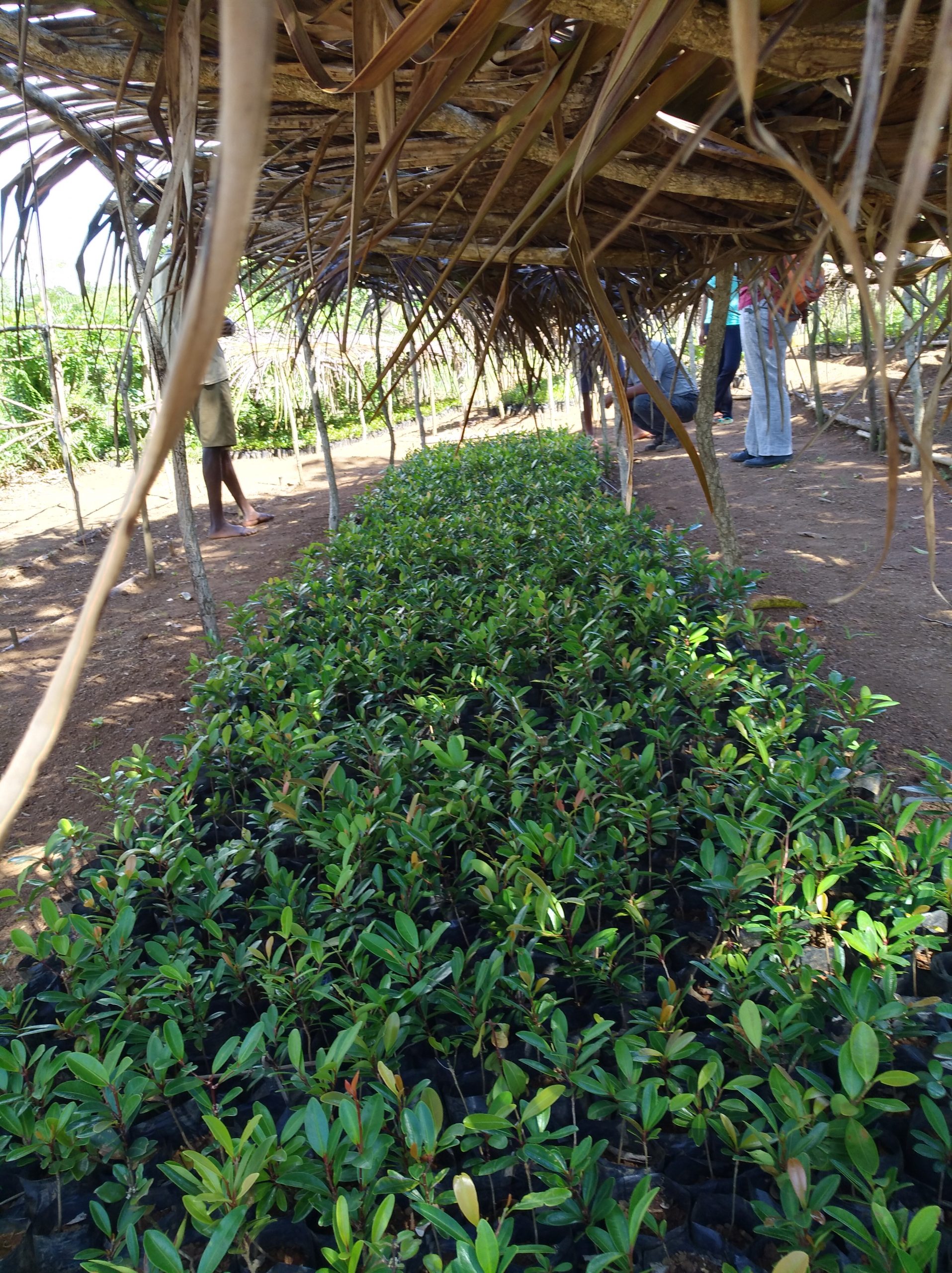
Agnalazaha Forest is home to numerous plant species typical of coastal forests, several of which are endemic to this southeastern region. A total of 246 floristic species are recorded there, 198 of which are endemic to Madagascar and 10 species are endemic to the region.
The avifauna is represented by 66 species. The group of Lemurs is represented by 5 species including the Eulemur cinereiceps, endemic to the region.