Flagship Species
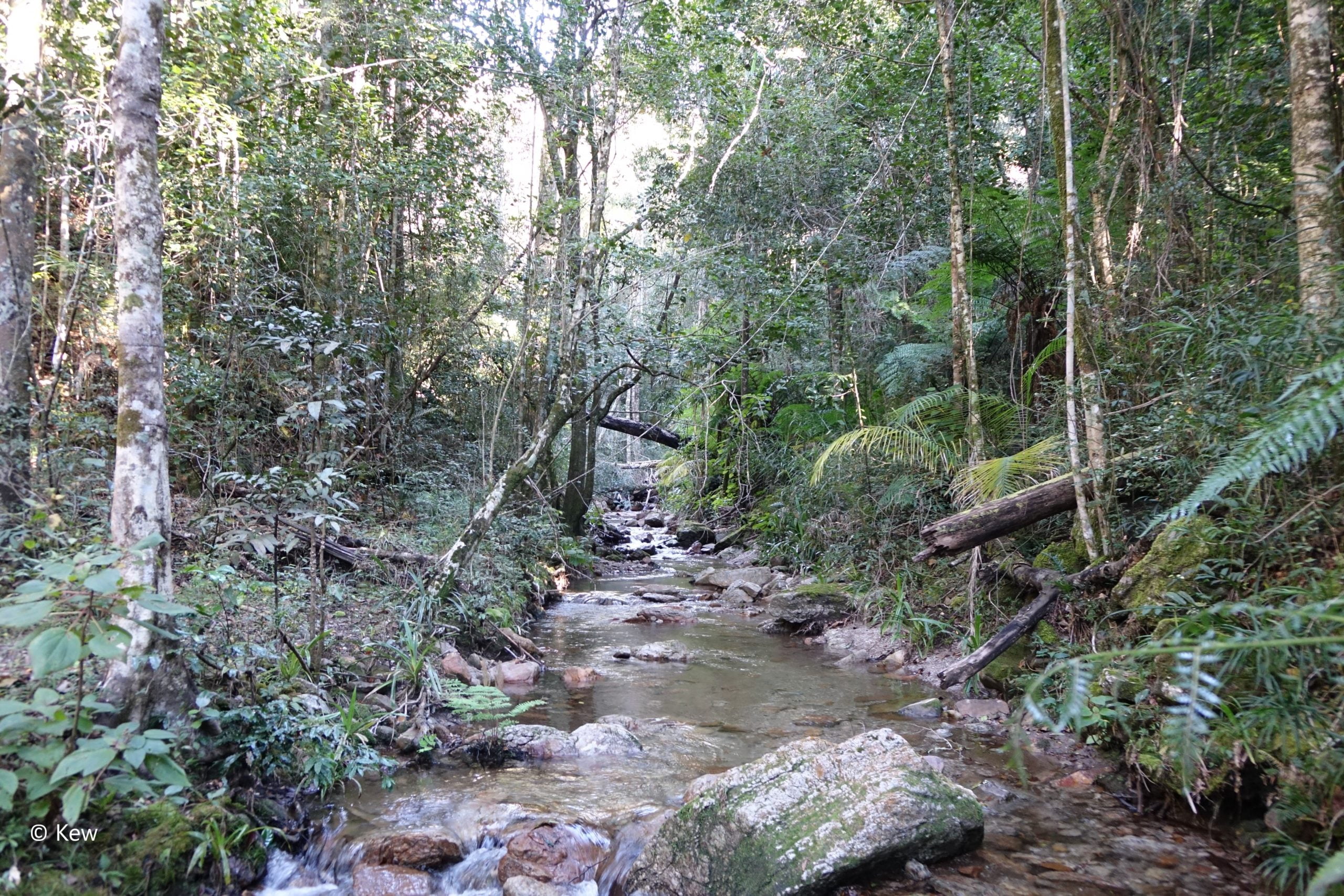
The Itremo Massif is made up of rocky substrates, wooded savannas with open canopy tapia forests and gallery forests.
There are currently more than 550 species of plants, 59 species of birds, 17 species of amphibians and 14 species of reptiles.